Propranolol: A Non-Selective Beta Blocker for Cardiovascular, Neurological, and Stress-Related Disorders
🩺 What is Propranolol?
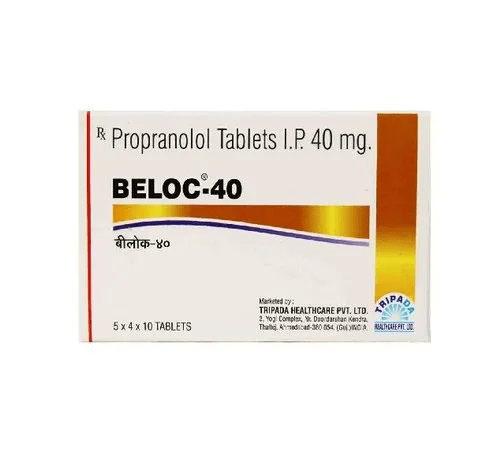
Propranolol is a first-generation, non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker used to treat a wide range of conditions including hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, anxietye migraine prophylaxis. It was the first beta blocker developed and remains a foundational agent in cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric medicine.
⚙️ Mecanismo de ação
Propranolol blocks both β1 and β2-adrenergic receptors:
- β1 blockade (heart): Decreases heart rate, contractility, and cardiac output → reduces blood pressure and oxygen demand.
- β2 blockade (lungs, vasculature): May cause bronchoconstriction, peripheral vasoconstriction, and metabolic effects (e.g., decreased glycogenolysis).
Its lipophilic nature also allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier, contributing to central nervous system effects like anxiolysis and tremor control.
📋 Indicações
Cardiovascular:
- Hypertension (alone or in combination)
- Angina pectoris
- Supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g., atrial fibrillation)
- Post-myocardial infarction (MI) secondary prevention
- Hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
Neurological & Psychiatric:
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Essential tremor
- Anxiety (especially performance anxiety)
- PTSD-related symptoms (off-label)
Other Uses:
- Hyperthyroidism (adjunctive)
- Pheochromocytoma (with alpha-blockers)
- Portal hypertension (reduces risk of esophageal variceal bleeding)
💊 Dosagem e administração
Typical adult dosing regimens:
| Indication | Dose Range |
|---|---|
| Hipertensão | 40–160 mg BID |
| Migraine prophylaxis | 80–160 mg/day |
| Anxiety (situational) | 10–40 mg 30 mins before event |
| Essential tremor | 40–120 mg/day |
| Post-MI | 180–240 mg/day |

Avaliações
Ainda não existem avaliações.